| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 스택
- 코딩
- 시간 복잡도
- 코딩좀알려주라
- FIFO
- 동적 배열
- 대학생
- 리스트
- 큐
- IT
- CSS
- 모각코
- LIFO
- 코뮤니티
- 자료구조
- 파이썬
- 수파자
- 연결 리스트
- HTML
- 프로그래밍
- 서포터즈
- 양방향 연결 리스트
- 선형 자료 구조
- 한방향 연결 리스트
- 한국외대
- 웹 기초
- O(1)
- 대외활동
- 알고리즘
- 한국대학생IT경영학회
- Today
- Total
대학생 쩡딱구리
3-2. 큐 본문
3-1. 스택
1. 스택이란? 스택(Stack)이란 한 쪽 끝에서만 자료를 넣거나 뺄 수 있는 선형 자료 구조이다. 스택은 LIFO(Last In First Out) 형태의 자료구조로, 가장 최근에 저장된 값 다음에 자료가 저장되고(push), �
jjeongttakgoori.tistory.com
스택에 대한 내용은 이 게시물에 있다.
1. 큐
가장 나중에 들어간 자료가 가장 먼저 나오는 스택과 달리 큐(Queue)는 FIFO(First In, First Out) 형태 자료 구조로, 가장 먼저 넣은 것이 가장 먼저 나온다. 달리 말하면 큐는 한쪽 끝에서는 자료를 넣고 한 쪽 끝에서 자료를 꺼내는 선형 자료구조를 말한다. 큐에서는 가장 최근에 저장된 값 다음에 자료가 저장되며(Enqueue), 가장 오래 전에 저장된 값부터 나간다.(Dequeue)

큐는 요청된 순서대로 일을 처리할 때 쓰인다. 티켓 구매를 위해 줄을 서는 것, 서비스 센터에서 전화 연결이 배분되는 것 모두 큐와 비슷한 일상 속 예시이다.
2. 큐의 기본 연산
| Operation | Comment |
| Q.enqueue(e) | back에 요소 e를 추가 |
| Q.dequeue(e) | - Front의 요소를 반환하면서 제거 - 큐가 비어 있으면 error 생성 |
| Q.first() | - Front의 요소를 반환(단, 요소를 제거하지는 않음) - 큐가 비어 있으면 error 생성 |
| Q.is_empty() | 큐가 비어 있으면 True 반환 |
| len(Q) | 큐에 저장된 요소의 개수를 반환 |
3. 배열 기반의 큐 구현

리스트로 큐를 구현해보자. 큐에선 Front와 back의 인덱스가 계속 한방향으로 증가하므로 원형 배열을 이용하자! 원형 배열(Circular Array)로 설계 시 배열의 양끝이 증가하거나 감소할 경우 설계하면 연산 효율을 높일 수 있다.

원형 큐는 원형 배열에서 인덱스가 증가하는 방향으로 front와 back을 이동한다. 아래 그림(enqueue)을 보도록 하자.

4. ArrayQueue 클래스
전체 코드를 본 후, 부분마다 설명한다.
class Empty(Exception):
"""Error attempting to access an element from an empty container."""
pass
class ArrayQueue:
"""FIFO queue implementation using a Python list as underlying storage."""
DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 # moderate capacity for all new queues
def __init__(self):
"""Create an empty list."""
self._data = [None] * ArrayQueue.DEFAULT_CAPACITY
self._size = 0
self._front = 0
def __len__(self):
"""Return the number of elements in the queue."""
return self._size
def is_empty():
"""Return True if the queue is empty."""
return self._size == 0
def first(self):
"""Return (but do not remove) the element at the front of the queue.
Raise Empty exception if the queue is empty."""
if self.is_empty():
raise Empty('Queue is empty')
raise self._data[self._front] # front has been realigned
def Dequeue(self):
"""Remove and return the first element of the queue (i.e., FIFO).
Raise Empty exception if the queue is empty."""
if self.is_empty():
raise Empty('Queue is empty')
answer = self._data[self._front]
self._data[self._front] = None # help garbage collection
self._front = (self._front + 1) % len(self._data)
self._size -= 1
return answer
def enqueue(self, e):
"""Add an element to the back of queue."""
if self._size == len(self._data):
self._resize(2 * len(self.data)) # double the array size
avail = (self._front + self._size) % len(self._data)
self._data[avail] = e
self._size += 1
def _resize(self, cap):
"""Resize to a new list of capacity >= len(self)."""
old = self._data
self._data = [None] * cap
walk = self._front
for k in range(self._size):
self._data[k] = old[walk]
walk = (1 + walk) % len(old)
self._front = 01) 클래스 선언: 새로운 큐를 생성할 때 기본 리스트 크기를 DEFAULT_CAPACITY로 지정
class Empty(Exception):
"""Error attempting to access an element from an empty container."""
pass
class ArrayQueue:
"""FIFO queue implementation using a Python list as underlying storage."""
DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 # moderate capacity for all new queues2) 초기화
- self._data: 데이터를 관리하는 리스트
- self._size: 큐에 저장된 데이터 개수
- self._front: 큐의 front를 관리 (원형 큐인 경우 계속 front가 변경됨)
- back은 명시적으로 관리하지 않고 back = self._front + self._size - 1와 같이 계산
def __init__(self):
"""Create an empty list."""
self._data = [None] * ArrayQueue.DEFAULT_CAPACITY
self._size = 0
self._front = 03) 길이: self._size를 반환
def __len__(self):
"""Return the number of elements in the queue."""
return self._size4) 큐가 비어 있는지 확인: self._size == 0이면 True, 아니면 False로
def is_empty():
"""Return True if the queue is empty."""
return self._size == 05) 큐의 첫 번째 요소 반환: 큐가 비어 있으면 Empty 오류 발생. 비어 있지 않으면 front의 데이터 반환
def first(self):
"""Return (but do not remove) the element at the front of the queue.
Raise Empty exception if the queue is empty."""
if self.is_empty():
raise Empty('Queue is empty')
raise self._data[self._front] # front has been realigned 6) Dequeue:
- 큐가 비어 있으면 Empty 오류 발생
- front의 데이터를 반환하면서 요소를 삭제
- 요소 삭제 연산은 front를 한 칸 이동하고 크기는 1을 줄이는 형식으로 처리
- 단, front 이동 시 mod 연산을 통해 원형으로 이동(circular shift)
def Dequeue(self):
"""Remove and return the first element of the queue (i.e., FIFO).
Raise Empty exception if the queue is empty."""
if self.is_empty():
raise Empty('Queue is empty')
answer = self._data[self._front]
self._data[self._front] = None # help garbage collection
self._front = (self._front + 1) % len(self._data)
self._size -= 1
return answer7) Enqueue:
- 큐가 다 찼으면 크기를 두 배로 키움
- 큐에 요소를 추가하기 위해 back을 한 칸 이동해서 데이터를 추가하고 크기를 1 늘림
- 단, back 이동 시 mod 연산을 통해 원형으로 이동(circular shift)(avail로 지정)
def enqueue(self, e):
"""Add an element to the back of queue."""
if self._size == len(self._data):
self._resize(2 * len(self.data)) # double the array size
avail = (self._front + self._size) % len(self._data)
self._data[avail] = e
self._size += 1
큐의 크기를 늘릴 때는 원형 배열의 순서에 맞게 데이터 위치를 앞쪽으로 재정렬한다.
재정렬을 하지 않으면 큐의 데이터의 순서 관계가 깨지게 된다.
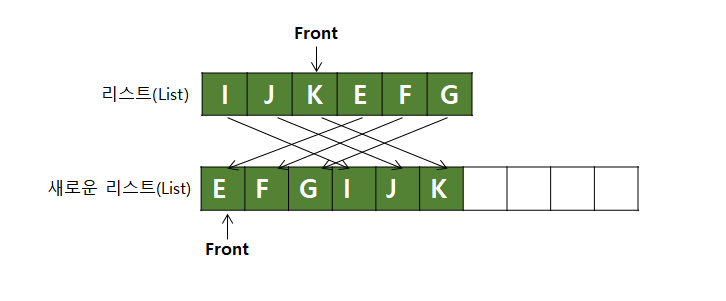
8) 리스트 크기 조절
- cap 크기의 새로운 리스트 생성
- 원래 리스트의 데이터를 새로운 리스트로 옮긴다.
- 단, front가 index = 0이 되도록 정렬
def _resize(self, cap):
"""Resize to a new list of capacity >= len(self)."""
old = self._data
self._data = [None] * cap
walk = self._front
for k in range(self._size):
self._data[k] = old[walk]
walk = (1 + walk) % len(old)
self._front = 0
5. 기본 연산 성능 분석
리스트로 큐를 구현하면 모든 연산이 O(1) 시간 복잡도를 갖는다.
| Operation | Running Time(amortized) |
| Q.enqueue() | O(1) |
| Q.dequeue() | O(1) |
| Q.first() | O(1) |
| Q.is_empty() | O(1) |
| len(Q) | O(1) |
큐와 덱을 모두 다루려고 했는데 너무 길어졌다. 바로 다음 게시물에서 덱을 짧게 다루겠다.
'STUDIES > DATA STRUCTURE' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4-1. 한방향 연결 리스트 (0) | 2020.10.19 |
|---|---|
| 3-3 덱 (0) | 2020.10.17 |
| 3-1. 스택 (0) | 2020.10.17 |
| 2-3. 분할 분석과 성능 분석 (0) | 2020.10.16 |
| 2-2. 동적 배열 (0) | 2020.10.15 |
